Showing posts with label ubuntu. Show all posts
Showing posts with label ubuntu. Show all posts
Tuesday 16 October 2012
Practical ls Command Examples For Fun & Profit
The power of linux lies in the shell through which we can perform complex job in no time. While the directory listing command 'ls' seems to be very simple command, the linux shell provides the power to use switches and pipes to do anything from terminal. Check out this list with practically useful examples using ls.
Any more example that fires up in your mind? Feel free to share over here ;)
Read more...
Display all files including hidden files/folders
ls -a
Display one file/folder per line
ls -1
Count number of files & folders
ls -1 | wc -l
Human readable file sizes (eg. Mb or Gb)
ls -lh
Alphabetically sort the listing
ls -X
Only list the folders in current directory
ls -d */
ls -p | grep /
ls -p | grep /
Display folders in current directory consisting certain patterns
ls -l D* | grep :$
ls -l *a* | grep :$
ls -l *a* | grep :$
List files by descending order of modification time
ls -lt
ls -l --sort=time #alternative long version
ls -l --sort=time #alternative long version
List files by descending order of creation time
ls -lct
List files in reverse order
ls -ltr
ls -l --sort=time --reverse #alternative long version
ls -l --sort=time --reverse #alternative long version
List files in descending order of file size
ls -lSh
ls -lh --sort=size
ls -lSh1 *.avi #find largest AVI file
rm `ls -S1 | head -1` #delete largest file in current folder
ls -lh --sort=size
ls -lSh1 *.avi #find largest AVI file
rm `ls -S1 | head -1` #delete largest file in current folder
List files in ascending order of file size
ls -lShr
ls -lh --sort=size --reverse #alternative long version
ls -lh --sort=size --reverse #alternative long version
Display directories in recursive manner
ls -R
Display the files/folders created today
ls -l --time-style=+%F | grep `date +%F`
Display the files/folders created this year
ls -l --time-style=+%y | grep `date +%y`
Any more example that fires up in your mind? Feel free to share over here ;)
Read more...
Practical ls Command Examples For Fun & Profit
2012-10-16T00:44:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday 15 October 2012
Useful Nautilus Shortcuts
Nautilus is a default file manager for GNOME Desktop and is used as the default file manager in several linux distros such as Ubuntu. I love nautilus because its simple, friendly, and clean, supports local as well as remote file systems over different protocols. Moreover, there are several useful shortcuts that make life easier while using nautilus.
Below is the list of the most helpful shortcuts for navigation and file management in the nautilus:
Ctrl + r: Refresh the current view
Ctrl + h: Toggle show/hide mode for hidden files
F9: Show/Hide the side pane
Ctrl + l: Activate location/url bar (You can then provide path to local or remote filesystems or quickly copy the absolute paths)
Alt + Up Arrow: Move up one directory level
Alt + Down Arrow: Move down one directory level (the directory to be entered should be selected for this to work)
Alt + Left Arrow: Go back to the previous folder in view
Alt + Right Arrow: Go forward
Ctrl + Shift + n: Create a new empty directory
Ctrl + (+ / -): Zoom in (+) or zoom out (-)
Ctrl + 0: Zoom to normal state
Alt + Enter: View selected file/folder properties
F2: Rename selected file/folder
Ctrl + Shift + Drag file/folder: Create symbolic link to file/folder
Ctrl + f: Search for files/folders
Ctrl + s: Select files based upon templates (eg. select all pdf files using *.pdf)
Ctrl + 1: Toggle view as icons
Ctrl + 2: Toggle view as lists
Ctrl + 3: Toggle compact view
Ctrl + w: Close current nautilus window
Ctrl + Shift + w: Current all open nautilus windows
Ctrl + T: Open new tab
Alt + HOME: Navigate to HOME folder
F6: Toggle between side pane and central pane
Know more shortcuts? Share as the comments :)
Read more...
Below is the list of the most helpful shortcuts for navigation and file management in the nautilus:
Ctrl + r: Refresh the current view
Ctrl + h: Toggle show/hide mode for hidden files
F9: Show/Hide the side pane
Ctrl + l: Activate location/url bar (You can then provide path to local or remote filesystems or quickly copy the absolute paths)
Alt + Up Arrow: Move up one directory level
Alt + Down Arrow: Move down one directory level (the directory to be entered should be selected for this to work)
Alt + Left Arrow: Go back to the previous folder in view
Alt + Right Arrow: Go forward
Ctrl + Shift + n: Create a new empty directory
Ctrl + (+ / -): Zoom in (+) or zoom out (-)
Ctrl + 0: Zoom to normal state
Alt + Enter: View selected file/folder properties
F2: Rename selected file/folder
Ctrl + Shift + Drag file/folder: Create symbolic link to file/folder
Ctrl + f: Search for files/folders
Ctrl + s: Select files based upon templates (eg. select all pdf files using *.pdf)
Ctrl + 1: Toggle view as icons
Ctrl + 2: Toggle view as lists
Ctrl + 3: Toggle compact view
Ctrl + w: Close current nautilus window
Ctrl + Shift + w: Current all open nautilus windows
Ctrl + T: Open new tab
Alt + HOME: Navigate to HOME folder
F6: Toggle between side pane and central pane
Know more shortcuts? Share as the comments :)
Read more...
Useful Nautilus Shortcuts
2012-10-15T17:51:00+05:45
Cool Samar
keyboard shortcuts|linux|nautilus|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
keyboard shortcuts,
linux,
nautilus,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Saturday 13 October 2012
Empty Trash From Command Line In Ubuntu
CLI is such a sexy piece so why bother using GUI, even for cleaning up your trash. In this post, you will see how you can empty trash in Ubuntu from command line.
The trash you see in GUI is nothing but just the view for the files deleted by users which are temporarily moved to the special location of user's home directory. For any user, the trash location is ~/.local/share/Trash/. That is, whatever a user deletes gets saved in this location.
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
The trash you see in GUI is nothing but just the view for the files deleted by users which are temporarily moved to the special location of user's home directory. For any user, the trash location is ~/.local/share/Trash/. That is, whatever a user deletes gets saved in this location.
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ rm -rf ~/.local/share/Trash/
I hope this becomes useful :)
Read more...
Empty Trash From Command Line In Ubuntu
2012-10-13T16:11:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.04|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.04,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
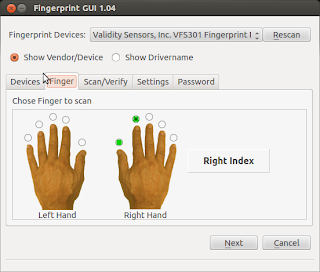
Enable Fingerprint Authentication In Ubuntu
So you got fingerprint reader in your device but have not been able to use it under ubuntu? Follow this How To to enable fingerprint authentication in ubuntu using the Fingerprint GUI from fingerprints reader integration team.
First make sure your fingerprint hardware is supported. You can check for the vendor and device ID by entering the following command:
This link provides the list of the supported fingerprint readers.
Installation is easy. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
You will have to restart the system or log out the session and login back to use and configure the fingerprint GUI.
Press Alt + F2 and type fingerprint-gui. From this GUI, you can configure and enroll your fingerprints.
Read more...
First make sure your fingerprint hardware is supported. You can check for the vendor and device ID by entering the following command:
samar@TG:~$ lsusb | grep -i finger | awk -F " " '{print $6}'
138a:0005
138a:0005
Installation is easy. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:fingerprint/fingerprint-gui
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libbsapi policykit-1-fingerprint-gui fingerprint-gui
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libbsapi policykit-1-fingerprint-gui fingerprint-gui
You will have to restart the system or log out the session and login back to use and configure the fingerprint GUI.
Press Alt + F2 and type fingerprint-gui. From this GUI, you can configure and enroll your fingerprints.
Read more...
Enable Fingerprint Authentication In Ubuntu
2012-10-13T10:11:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fingerprint|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
fingerprint,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Add Google Search Support In Gnome-Terminal
Gnome-terminal is my favorite thing in my system and recently I came to know that I could add google search support in gnome-terminal which is totally awesome. Ubuntu Tweak already includes the google search support but if you want google search in your terminal without the whole ubuntu tweak, you can follow this guide.
All you need to do is add the PPA and you can easily install the gnome-terminal with google search support. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
Credits: Ubuntu Tweak
Read more...
All you need to do is add the PPA and you can easily install the gnome-terminal with google search support. Fire up the terminal and enter the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tualatrix/personal
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gnome-terminal
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gnome-terminal
Credits: Ubuntu Tweak
Read more...
Add Google Search Support In Gnome-Terminal
2012-10-13T09:22:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Tuesday 2 October 2012
Binary, Hex, Octal and Decimal Conversion Under Linux
Base conversions are easy with linux CLI. No need of fancy GUI-based calculator to perform base conversions when there is our favorite linux terminal.
We will be using bc, a calculator language that supports arbitrary precision numbers with interactive execution of statements. We will exploit the pipelining feature of shell and will let the bc process our query to convert the numbers from one base to other.
As seen in all the examples above, the conversion to decimal numbers does not require you to specify the obase as obase defaults to decimal. The same thing applies for ibase i.e. ibase defaults to decimal base by default as seen in the examples below.
Now lets try some conversion with decimal numbers as the input base.
Below are few more examples of base conversions to clarify the use of the command.
I hope this is helpful ;-)
Read more...
We will be using bc, a calculator language that supports arbitrary precision numbers with interactive execution of statements. We will exploit the pipelining feature of shell and will let the bc process our query to convert the numbers from one base to other.
From binary to decimal
The syntax is obvious and we will follow the similar syntax for all the conversions. In this first example, we are converting the binary number 1101101 from input base binary to decimal(obase defaults to decimal unless specified).
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=2;1101101" | bc
109
109
From octal to decimal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=8;1101101" | bc
295489
295489
From Hexadecimal to decimal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=16;A1F3DF" | bc
10613727
10613727
From N-base to decimal
All you need to do is provide the appropriate ibase value (eg. ibase=4 for 4-base to decimal conversion).
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=16;A1F3DF" | bc
10613727
10613727
As seen in all the examples above, the conversion to decimal numbers does not require you to specify the obase as obase defaults to decimal. The same thing applies for ibase i.e. ibase defaults to decimal base by default as seen in the examples below.
Now lets try some conversion with decimal numbers as the input base.
From decimal to binary
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=2;109" | bc
1101101
1101101
From decimal to octal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=8;295489" | bc
1101101
1101101
From decimal to hexadecimal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=16;10613727" | bc
A1F3DF
A1F3DF
From decimal to N-base
All you need to do is provide the appropriate obase value (eg. obase=4 for decimal to 4-base conversion).
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "obase=4;121" | bc
1321
1321
Below are few more examples of base conversions to clarify the use of the command.
From binary to octal
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=2;obase=8;1111" | bc
17
17
From hexadecimal to binary
samar@samar-Techgaun:~$ echo "ibase=16;obase=2;AFBE" | bc
1010111110111110
1010111110111110
I hope this is helpful ;-)
Read more...
Binary, Hex, Octal and Decimal Conversion Under Linux
2012-10-02T22:12:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|mathematics|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
mathematics,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 28 September 2012
Ubuntu 12.10 Beta 2 Released
The ubuntu developers have just released the Beta 2 of Ubuntu 12.10 Quantal Quetzal which gives the preview of the next version of ubuntu. The final ubuntu 12.10 release is scheduled for 18th October this year.
The Beta 2 release is intended to give the preview of how the final release of Quantal Quetzal will be like. The previous beta 1 release was released on 6th September.
As always, Ubuntu has chosen the Quetzal as codename for Ubuntu 12.10. According to Wikipedia, Quetzals are strikingly colored birds in the trogon family. They are found in forests and woodlands, especially in humid highlands, with the five species from the genus Pharomachrus being exclusively Neotropical, while the single Euptilotis species is almost entirely restricted to western Mexico.
Like we heard earlier, Ubuntu 12.10 releases are no longer available as Live CD.
Download Quantal Quetzal 12.10 Beta 2 Release
Read more...
As always, Ubuntu has chosen the Quetzal as codename for Ubuntu 12.10. According to Wikipedia, Quetzals are strikingly colored birds in the trogon family. They are found in forests and woodlands, especially in humid highlands, with the five species from the genus Pharomachrus being exclusively Neotropical, while the single Euptilotis species is almost entirely restricted to western Mexico.
Like we heard earlier, Ubuntu 12.10 releases are no longer available as Live CD.
Download Quantal Quetzal 12.10 Beta 2 Release
Read more...
Ubuntu 12.10 Beta 2 Released
2012-09-28T16:21:00+05:45
Cool Samar
news|quantal quetzal|ubuntu|ubuntu 12.10|
Comments
Labels:
news,
quantal quetzal,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 12.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 14 September 2012
How To Find The Location Of Command In Linux
Sometimes you need to find the pathnames or locations of commands you use frequently. In this post, I am going to discuss two useful commands that are useful for locating Linux commands.
The first command to locate the Linux commands is which. This command returns the pathnames of the files or links. However, it does not follow the symbolic links.
You can also find the pathnames of multiple commands at once using which command.
The other command is type command which is useful to determine if a command is an alias, a built-in command or an independent command.
You can play more with the type command. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
The first command to locate the Linux commands is which. This command returns the pathnames of the files or links. However, it does not follow the symbolic links.
samar@Techgaun:~$ which bash
/bin/bash
/bin/bash
You can also find the pathnames of multiple commands at once using which command.
samar@Techgaun:~$ which -a bash cat ls iftop
/bin/bash
/bin/cat
/bin/ls
/usr/sbin/iftop
/bin/bash
/bin/cat
/bin/ls
/usr/sbin/iftop
The other command is type command which is useful to determine if a command is an alias, a built-in command or an independent command.
samar@Techgaun:~$ type gedit
gedit is /usr/bin/gedit
samar@Techgaun:~$ type grep
grep is aliased to `grep --color=auto'
samar@Techgaun:~$ type -t iftop
file
gedit is /usr/bin/gedit
samar@Techgaun:~$ type grep
grep is aliased to `grep --color=auto'
samar@Techgaun:~$ type -t iftop
file
You can play more with the type command. I hope this helps :)
Read more...
How To Find The Location Of Command In Linux
2012-09-14T01:05:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Tuesday 11 September 2012
Ubuntu Desktop Edition No More In LiveCD
The ubuntu team has announced that they have dropped the LiveCD option for Ubuntu and now onwards Ubuntu will be available as a single 800MB image that can be used from USB or DVD.
The mailing list reads "For the client, this release now has a consolidated Ubuntu image. There is no longer a traditional CD sized image, DVD or alternate image, but rather a single 800MB Ubuntu image that can be used from USB or DVD. This change does not affect Ubuntu Server, which remains a traditional CD sized image.
That is, starting from Ubuntu 12.10 "Quantal Quetzal", we will have a single 800 MB disk image that can only be used with USB or DVD. The decision does not seem to affect Ubuntu's user base since DVDs and USBs are getting cheaper and LiveUSBs are being popular these days.
Read more...
The mailing list reads "For the client, this release now has a consolidated Ubuntu image. There is no longer a traditional CD sized image, DVD or alternate image, but rather a single 800MB Ubuntu image that can be used from USB or DVD. This change does not affect Ubuntu Server, which remains a traditional CD sized image.
That is, starting from Ubuntu 12.10 "Quantal Quetzal", we will have a single 800 MB disk image that can only be used with USB or DVD. The decision does not seem to affect Ubuntu's user base since DVDs and USBs are getting cheaper and LiveUSBs are being popular these days.
Read more...
Ubuntu Desktop Edition No More In LiveCD
2012-09-11T16:39:00+05:45
Cool Samar
news|ubuntu|
Comments
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday 3 September 2012
Preventing Accidental Overwriting Of Files In Bash Shell
How many times has this happened to you? It used to happen once in a while with me. A Linux user learns to use the redirection operators such as '>' and '>>' but accidental overwriting starts to become common in commands you use and shell scripts you write.
The accidental overwriting of files that happens unintentionally is known as clobbering and it commonly happens while using the '>' redirection operator.
In the above example, the mycmd clobbers any existing data in the myfile file if that file exists already. Worse things may happen sometime. Imagine accidentally typing
instead of possibly using other redirection operators (like >> or <). Thankfully, you could recover /etc/passwd from either /etc/passwd- or /var/backups/passwd.bak if you hadn't rm'd these files.
To prevent such accidental overwriting, we can set the noclobber environment variable. Below is a session of enabling this variable:
As seen above, you have to turn on the noclobber variable using the set -o noclobber command in your shell. However, you might want to intentionally overwrite contents of certain files even when the noclobber is turned on.
Notice the >| in place of your normal > redirection operator. Using this operator, you can however overwrite the existing files even if the noclobber is turned on.
If you want to turn off the noclobber variable, type the following:
You can also permanently turn on the noclobber by the following command:
Moreover, such accidental overwriting can be prevented by enabling the interactive mode which is available in most of the linux commands. For example, you can write the alias for many commands that are likely to cause accidental overwriting. See some examples of aliases below:
You could even keep these aliases in your ~/.bashrc file permanently. Enabling such interactive modes by default in the commands that are more likely to cause accidental overwriting can prevent clobbering in many cases.
I hope this proves useful to you :)
Read more...
The accidental overwriting of files that happens unintentionally is known as clobbering and it commonly happens while using the '>' redirection operator.
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd > myfile
In the above example, the mycmd clobbers any existing data in the myfile file if that file exists already. Worse things may happen sometime. Imagine accidentally typing
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd > /etc/passwd
instead of possibly using other redirection operators (like >> or <). Thankfully, you could recover /etc/passwd from either /etc/passwd- or /var/backups/passwd.bak if you hadn't rm'd these files.
To prevent such accidental overwriting, we can set the noclobber environment variable. Below is a session of enabling this variable:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "www.techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Overwriting techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ set -o noclobber
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Retrying to overwrite" > myfile
-bash: myfile: cannot overwrite existing file
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Overwriting techgaun.com" > myfile
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ set -o noclobber
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$ echo "Retrying to overwrite" > myfile
-bash: myfile: cannot overwrite existing file
As seen above, you have to turn on the noclobber variable using the set -o noclobber command in your shell. However, you might want to intentionally overwrite contents of certain files even when the noclobber is turned on.
samar@Techgaun:~$ mycmd >| myfile
Notice the >| in place of your normal > redirection operator. Using this operator, you can however overwrite the existing files even if the noclobber is turned on.
If you want to turn off the noclobber variable, type the following:
samar@Techgaun:~$ set +o noclobber
You can also permanently turn on the noclobber by the following command:
samar@Techgaun:~$ echo "set -o noclobber" >> ~/.bashrc
Moreover, such accidental overwriting can be prevented by enabling the interactive mode which is available in most of the linux commands. For example, you can write the alias for many commands that are likely to cause accidental overwriting. See some examples of aliases below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias rm=rm -i
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias mv=mv -i
samar@Techgaun:~$ alias mv=mv -i
You could even keep these aliases in your ~/.bashrc file permanently. Enabling such interactive modes by default in the commands that are more likely to cause accidental overwriting can prevent clobbering in many cases.
I hope this proves useful to you :)
Read more...
Preventing Accidental Overwriting Of Files In Bash Shell
2012-09-03T22:56:00+05:45
Cool Samar
bash|command line|fedora|filesystem|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
bash,
command line,
fedora,
filesystem,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday 2 September 2012
How To Search Manual Pages In Linux
Linux system consists of hundreds of binaries, several syscalls, and other stuffs that do have manual page. What if you want to locate or find the commands by searching through the manual pages? In this post, I am going to talk about one such useful command to search through the manual page names and short descriptions.
The command I am talking about is the apropos command. The best way to learn any linux command is to read its corresponding manual and go through the help (-h or --help) so lets poke through the help of apropos itself.
Particularly, the -e switch is quite useful to filter out your search. See the example below:
Each command has its associated short description and the apropos command searches the short description section of appropriate manual page for the provided keyword. You can also specify the search keywords in the form of regular expression for more flexibility. I hope this command counts as useful one :)
Read more...
The command I am talking about is the apropos command. The best way to learn any linux command is to read its corresponding manual and go through the help (-h or --help) so lets poke through the help of apropos itself.
samar@Techgaun:~$ apropos -h
Usage: apropos [OPTION...] KEYWORD...
-d, --debug emit debugging messages
-v, --verbose print verbose warning messages
-e, --exact search each keyword for exact match
-r, --regex interpret each keyword as a regex
-w, --wildcard the keyword(s) contain wildcards
-a, --and require all keywords to match
-l, --long do not trim output to terminal width
-C, --config-file=FILE use this user configuration file
-L, --locale=LOCALE define the locale for this search
-m, --systems=SYSTEM use manual pages from other systems
-M, --manpath=PATH set search path for manual pages to PATH
-s, --section=SECTION search only this section
-?, --help give this help list
--usage give a short usage message
-V, --version print program version
Mandatory or optional arguments to long options are also mandatory or optional
for any corresponding short options.
The --regex option is enabled by default.
Report bugs to cjwatson@debian.org.
Particularly, the -e switch is quite useful to filter out your search. See the example below:
samar@Techgaun:~$ apropos -e tar bf_tar (1) - shell script to write a tar file of a bogofilter direc... bf_tar-bdb (1) - shell script to write a tar file of a bogofilter direc... git-tar-tree (1) - Create a tar archive of the files in the named tree ob... lz (1) - gunzips and shows a listing of a gzip'd tar'd archive mxtar (1) - Wrapper for using GNU tar directly from a floppy disk ptar (1) - a tar-like program written in perl tar (1) - The GNU version of the tar archiving utility tar (5) - format of tape archive files tgz (1) - makes a gzip'd tar archive uz (1) - gunzips and extracts a gzip'd tar'd archive
Each command has its associated short description and the apropos command searches the short description section of appropriate manual page for the provided keyword. You can also specify the search keywords in the form of regular expression for more flexibility. I hope this command counts as useful one :)
Read more...
How To Search Manual Pages In Linux
2012-09-02T02:07:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Thursday 30 August 2012
Ubuntu "Precise Pangolin" 12.04.1 LTS Released
After few months of release of Precise Pangolin, the Canonical and ubuntu developers have finally released the version 12.04.1 of Long Term Support (LTS) of Ubuntu for desktop, server, cloud and core products.
For your information, each new LTS version is released every 2 years. Starting with Ubuntu 12.04 LTS, both desktop and server versions will receive 5 years support. Earlier versions received 3 years support for desktop version and 5 years support for server version.
Among all the changes, the most notable one is the support for Calxeda ECX-1000 SoC family for supporting low-energy hyper-scale data centre servers.
The Ubuntu Cloud Archive also makes its debut - essentially an online software repository from which administrators can download the latest versions of OpenStack for use with the latest long-term support (LTS) release of Ubuntu.
Certified 12.04.1 Ubuntu Cloud images are now available on Amazon Web Services and will soon be posted to Windows Azure as well.
You can follow the detailed Release Announcement and Change Summary for Ubuntu 12.04.1 LTS.
You can download Ubuntu 12.04 LTS from HERE.
Read more...
For your information, each new LTS version is released every 2 years. Starting with Ubuntu 12.04 LTS, both desktop and server versions will receive 5 years support. Earlier versions received 3 years support for desktop version and 5 years support for server version.
Among all the changes, the most notable one is the support for Calxeda ECX-1000 SoC family for supporting low-energy hyper-scale data centre servers.
The Ubuntu Cloud Archive also makes its debut - essentially an online software repository from which administrators can download the latest versions of OpenStack for use with the latest long-term support (LTS) release of Ubuntu.
Certified 12.04.1 Ubuntu Cloud images are now available on Amazon Web Services and will soon be posted to Windows Azure as well.
You can follow the detailed Release Announcement and Change Summary for Ubuntu 12.04.1 LTS.
You can download Ubuntu 12.04 LTS from HERE.
Read more...
Ubuntu "Precise Pangolin" 12.04.1 LTS Released
2012-08-30T00:07:00+05:45
Cool Samar
news|ubuntu|
Comments
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday 27 August 2012
Install XAMPP 1.8 From PPA In Ubuntu
Since apache friends has released the v. 1.8 of XAMPP for linux and windows, its important you guys upgrade your XAMPP. In this post, you will find the instructions to install XAMPP 1.8 from PPA.
The most important updates of v. 1.8.0 of XAMPP are: Apache 2.4.2, MySQL 5.5.25a, PHP 5.4.4, and phpMyAdmin 3.5.1. Since the software components are updated, I strongly recommend to upgrade your XAMPP.
All you have to do is follow the following steps in order:
Alternatively, you can download the tar file for XAMPP from Apache Friends and follow their instructions to install XAMPP 1.8.0. In case you're looking for upgrading your previous XAMPP installation, be sure to follow this How To.
I hope this helps :)
Read more...
The most important updates of v. 1.8.0 of XAMPP are: Apache 2.4.2, MySQL 5.5.25a, PHP 5.4.4, and phpMyAdmin 3.5.1. Since the software components are updated, I strongly recommend to upgrade your XAMPP.
All you have to do is follow the following steps in order:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:upubuntu-com/xampp
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install xampp
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install xampp
Alternatively, you can download the tar file for XAMPP from Apache Friends and follow their instructions to install XAMPP 1.8.0. In case you're looking for upgrading your previous XAMPP installation, be sure to follow this How To.
I hope this helps :)
Read more...
Install XAMPP 1.8 From PPA In Ubuntu
2012-08-27T22:56:00+05:45
Cool Samar
apache|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|xampp|
Comments
Labels:
apache,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
xampp
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
How To Manually Install Flash Player 11 In Linux
This post will provide a step by step instructions for installing flash player 11 plugin in ubuntu 11.04 and other different versions and distros. This will be helpful for everybody who are having trouble with the software center like I had.
Make sure no firefox process is running and then fire up the terminal and type the following commands in order:
Once you have finished copying the shared object and other necessary files in their respective target directories, you can open the firefox and you're good to go. :)
Read more...
Make sure no firefox process is running and then fire up the terminal and type the following commands in order:
mkdir -p ~/flash && cd ~/flash
wget http://archive.canonical.com/pool/partner/a/adobe-flashplugin/adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
tar -zxvf adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
sudo cp -r libflashplayer.so /usr/lib/firefox/plugins
sudo cp -r usr/* /usr
wget http://archive.canonical.com/pool/partner/a/adobe-flashplugin/adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
tar -zxvf adobe-flashplugin_11.2.202.238.orig.tar.gz
sudo cp -r libflashplayer.so /usr/lib/firefox/plugins
sudo cp -r usr/* /usr
Once you have finished copying the shared object and other necessary files in their respective target directories, you can open the firefox and you're good to go. :)
Read more...
How To Manually Install Flash Player 11 In Linux
2012-08-27T22:22:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|internet|linux|mozilla firefox|plugin|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|web|
Comments
Labels:
fedora,
internet,
linux,
mozilla firefox,
plugin,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
web
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday 13 August 2012
Screen Recording Software Solutions For Linux
Windows users have several options to choose from when it comes to the desktop recording (and only paid ones are good generally) but Linux users have fewer options but robust, simple, and best of all, free and open source desktop screen recording tools that we can trust on.
Below are some of the screen recording tools you might want to try:
recordMyDesktop is a desktop session recorder for GNU/Linux written in C. recordMyDesktop itself is a command-line tool and few GUI frontends are also available for this tool. There are two frontends, written in python with pyGtk (gtk-recordMyDesktop) and pyQt4 (qt-recordMyDesktop). recordMyDesktop offers also the ability to record audio through ALSA, OSS or the JACK audio server. Also, recordMyDesktop produces files using only open formats. These are theora for video and vorbis for audio, using the ogg container.
Installation under debian and ubuntu:
XVidCap is a small tool to capture things going on on an X-Windows display to either individual frames or an MPEG video. It enables you to capture videos off your X-Window desktop for illustration or documentation purposes.It is intended to be a standards-based alternative to tools like Lotus ScreenCam.
Istanbul is a desktop session recorder for the Free Desktop. It records your session into an Ogg Theora video file. To start the recording, you click on its icon in the notification area. To stop you click its icon again. It works on GNOME, KDE, XFCE and others. It was named so as a tribute to Liverpool's 5th European Cup triumph in Istanbul on May 25th 2005.
Vnc2flv is a cross-platform screen recording tool for UNIX, Windows or Mac. It captures a VNC desktop session (either your own screen or a remote computer) and saves as a Flash Video (FLV) file.
Wink is a Tutorial and Presentation creation software, primarily aimed at creating tutorials on how to use software (like a tutor for MS-Word/Excel etc). Using Wink you can capture screenshots, add explanations boxes, buttons, titles etc and generate a highly effective tutorial for your users. It requires GTK 2.4 or higher and unfortunately is just a freeware(could not find any source code for it).
Screenkast is a screen capturing program that records your screen-activities, supports commentboxes and exports to all video formats.
If you got any more suggestions, please drop the comment. :)
Read more...
Below are some of the screen recording tools you might want to try:
recordMyDesktop
recordMyDesktop is a desktop session recorder for GNU/Linux written in C. recordMyDesktop itself is a command-line tool and few GUI frontends are also available for this tool. There are two frontends, written in python with pyGtk (gtk-recordMyDesktop) and pyQt4 (qt-recordMyDesktop). recordMyDesktop offers also the ability to record audio through ALSA, OSS or the JACK audio server. Also, recordMyDesktop produces files using only open formats. These are theora for video and vorbis for audio, using the ogg container.
Installation under debian and ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install gtk-recordmydesktop
XVidCap
XVidCap is a small tool to capture things going on on an X-Windows display to either individual frames or an MPEG video. It enables you to capture videos off your X-Window desktop for illustration or documentation purposes.It is intended to be a standards-based alternative to tools like Lotus ScreenCam.
sudo apt-get install xvidcap
Istanbul
Istanbul is a desktop session recorder for the Free Desktop. It records your session into an Ogg Theora video file. To start the recording, you click on its icon in the notification area. To stop you click its icon again. It works on GNOME, KDE, XFCE and others. It was named so as a tribute to Liverpool's 5th European Cup triumph in Istanbul on May 25th 2005.
sudo apt-get install istanbul
Vnc2Flv
Vnc2flv is a cross-platform screen recording tool for UNIX, Windows or Mac. It captures a VNC desktop session (either your own screen or a remote computer) and saves as a Flash Video (FLV) file.
Wink
Wink is a Tutorial and Presentation creation software, primarily aimed at creating tutorials on how to use software (like a tutor for MS-Word/Excel etc). Using Wink you can capture screenshots, add explanations boxes, buttons, titles etc and generate a highly effective tutorial for your users. It requires GTK 2.4 or higher and unfortunately is just a freeware(could not find any source code for it).
Screenkast
Screenkast is a screen capturing program that records your screen-activities, supports commentboxes and exports to all video formats.
If you got any more suggestions, please drop the comment. :)
Read more...
Screen Recording Software Solutions For Linux
2012-08-13T17:21:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|linux|software|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|video|
Comments
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 27 July 2012
Determine Your SATA Disk Model And Vendor In Ubuntu
Sometimes you need to determine the model and vendor of your hard disk and here is the small tips on how to find those information.
All you have to do is type one of the following commands for the respective outputs:
I hope this becomes useful sometimes. :)
Read more...
All you have to do is type one of the following commands for the respective outputs:
cat /sys/class/block/sda/device/model
cat /sys/class/block/sda/device/vendor
Read more...
Determine Your SATA Disk Model And Vendor In Ubuntu
2012-07-27T21:36:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Wednesday 18 July 2012
Why Alias Command With Itself
Aliasing the command to itself to suppress the original functionality of the command and provide it new added sets of functionality can come quite handy for linux users and administrators.
If you have been using linux shell for a while, I'm pretty sure you are now familiar with the `ls` command, if not I think you have just learnt to use man pages. Probably you've been using `ls -l` command to list files with the files size as well. Too bad, you won't just be able to instantly make the sense of the file size displayed using this command so why not alias `ls` command to always provide human readable file sizes. So here is my alias:
This is what I always want to see as the output with `ls` command. The same kind of alias can be used with `du` and `df` commands. There are number of other cases where aliasing a command with itself is good choice.
Another example is the less command. By default, you need to press q to exit less which can be quite annoying if the entire content can fit in a single screen. However, adding -F flag will gracefully quit after displaying the content if the content fits in a single screen. So I have my alias for less as below:
If something shoots in your mind, feel free to share here as a comment :)
Read more...
If you have been using linux shell for a while, I'm pretty sure you are now familiar with the `ls` command, if not I think you have just learnt to use man pages. Probably you've been using `ls -l` command to list files with the files size as well. Too bad, you won't just be able to instantly make the sense of the file size displayed using this command so why not alias `ls` command to always provide human readable file sizes. So here is my alias:
alias ls='ls -lh'
This is what I always want to see as the output with `ls` command. The same kind of alias can be used with `du` and `df` commands. There are number of other cases where aliasing a command with itself is good choice.
Another example is the less command. By default, you need to press q to exit less which can be quite annoying if the entire content can fit in a single screen. However, adding -F flag will gracefully quit after displaying the content if the content fits in a single screen. So I have my alias for less as below:
alias lesss='less -F'
If something shoots in your mind, feel free to share here as a comment :)
Read more...
Why Alias Command With Itself
2012-07-18T18:15:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 13 July 2012
Stack-based Directory Switching For Easy Reversal
So how many times have you used the `cd` command repeatedly to go back and forth of two or more directories. Probably you are already familiar to the `cd -` command which lets you switch between the current and the previous directory. But, many times this current and previous directory switching restriction will not suffice and hence a better option in such case is to use the `pushd` command instead of `cd`.
For example, just use the `pushd somedirA`, `pushd somedirB`, ... and like that. Now if you need to switch back, you can just use `popd` command and you'll be switching back easily. The `pushd` command saves the current directory path and then cds to the supplied path.
If you dig more, you'll come to know about the -n and -N switches you can combine with these commands so I will let you explore on this. Also, you can use the `dirs` command to view the stack of directories. If you are some computer student or enthusiast, you have already gotten an idea from a famous data structure called stack. Anyway, I hope this comes handy sometimes like it does to me :)
Read more...
For example, just use the `pushd somedirA`, `pushd somedirB`, ... and like that. Now if you need to switch back, you can just use `popd` command and you'll be switching back easily. The `pushd` command saves the current directory path and then cds to the supplied path.
If you dig more, you'll come to know about the -n and -N switches you can combine with these commands so I will let you explore on this. Also, you can use the `dirs` command to view the stack of directories. If you are some computer student or enthusiast, you have already gotten an idea from a famous data structure called stack. Anyway, I hope this comes handy sometimes like it does to me :)
Read more...
Stack-based Directory Switching For Easy Reversal
2012-07-13T12:20:00+05:45
Cool Samar
edubuntu|fedora|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
edubuntu,
fedora,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 6 July 2012
Fix "trying to overwrite '*', which is also in package *"
Today I was updating few stuffs in edubuntu and dpkg was continually throwing me the problem while trying to install kdelibs-data. The error read as "trying to overwrite 'A', which is also in package X" and the fix was pretty straightforward but still I thought it would help someone out there.
Below is the exact error I was getting while trying to install kdelibs5-data from the deb file.
The fix was pretty simple. Add the --force-overwrite switch in the dpkg command as below:
I hope this comes useful sometimes.
Read more...
Below is the exact error I was getting while trying to install kdelibs5-data from the deb file.
dpkg: error processing /var/cache/apt/archives/
kdelibs5-data_4%3a4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/share/polkit-1/actions
/org.kde.kcontrol.kcmremotewidgets.policy', which is also in package kdebase-runtime-data 4:4.6.5-0ubuntu1
kdelibs5-data_4%3a4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb (--unpack):
trying to overwrite '/usr/share/polkit-1/actions
/org.kde.kcontrol.kcmremotewidgets.policy', which is also in package kdebase-runtime-data 4:4.6.5-0ubuntu1
The fix was pretty simple. Add the --force-overwrite switch in the dpkg command as below:
dpkg -i --force-overwrite kdelibs5-data_4.4.5-0ubuntu1.2_all.deb
I hope this comes useful sometimes.
Read more...
Fix "trying to overwrite '*', which is also in package *"
2012-07-06T17:34:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|edubuntu|linux|ltsp|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
edubuntu,
linux,
ltsp,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 15 June 2012
How To Enable Use Of Htaccess In Apache In Ubuntu
This How To provides a detail on how to enable use of .htaccess file in apache in ubuntu and the similar flavors of linux distribution.
To enable use of .htaccess, you can edit the /etc/apache2/sites-available/default file. Search for the portion which contains the following lines or something similar to that(The bold line is almost always present):
All you have to do is change the bold line above to:
Now you will need to restart the apache service so that the effect of change in configuration takes place. Enter the following command to restart the apache service:
Now your .htaccess files will start to work in ubuntu. :)
Read more...
To enable use of .htaccess, you can edit the /etc/apache2/sites-available/default file. Search for the portion which contains the following lines or something similar to that(The bold line is almost always present):
<Directory /var/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
All you have to do is change the bold line above to:
<Directory /var/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
allow from all
</Directory>
Now you will need to restart the apache service so that the effect of change in configuration takes place. Enter the following command to restart the apache service:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo service apache2 reload
Now your .htaccess files will start to work in ubuntu. :)
Read more...
How To Enable Use Of Htaccess In Apache In Ubuntu
2012-06-15T21:53:00+05:45
Cool Samar
htaccess|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|
Comments
Labels:
htaccess,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)