Showing posts with label ubuntu 11.10. Show all posts
Showing posts with label ubuntu 11.10. Show all posts
Monday 11 June 2012
Graphical Frontends To Sopcast Client For Linux
As all of you know the official Sopcast client for linux is only the command line version and many people find it difficult to use the CLI version. However, many good people have made an effort to write the graphical frontends to the Sopcast client for linux. Here you will find some of such GUI frontends for sopcast.
Sopcast Player: SopCast Player is designed to be an easy to use Linux GUI front-end for the p2p streaming technology developed by SopCast. SopCast Player features an integrated video player, a channel guide, and bookmarks. Once SopCast Player is installed it simply "just works" with no required configuration.
qsopcast: qsopcast is a QT GUI front-end of the Linux command line executive of P2P TV sopcast.
gsopcast: gsopcast is a GTK based GUI front-end for p2p TV sopcast.
TV-Maxe: TV-MAXE is an application which provides the ability to watch TV stations and listen radio via different streams, such is SopCast. Currently it has a large number of channels, both romanian and international.
SCPlayer: SCPlayer is a simple and lightweight GUI frontend for sopcast supporting only linux GNOME3 platform.
Pysopcast: It is a simple GUI for sopcast made using PyGTK.
totem-sopcast: A totem plugin to let you browse and play sopcast streams.
wxsopcast: A sopcast GUI for linux written in python and wxPython. Note that the channel URL needs to be changed to http://www.sopcast.com/gchlxml at first.
jsopcast: jsopcast is a simple GUI to see P2P TV sopcast made in Java.
If you know of any other GUI frontend for sopcast, please feel free to leave a comment. :)
Read more...
Sopcast Player: SopCast Player is designed to be an easy to use Linux GUI front-end for the p2p streaming technology developed by SopCast. SopCast Player features an integrated video player, a channel guide, and bookmarks. Once SopCast Player is installed it simply "just works" with no required configuration.
qsopcast: qsopcast is a QT GUI front-end of the Linux command line executive of P2P TV sopcast.
gsopcast: gsopcast is a GTK based GUI front-end for p2p TV sopcast.
TV-Maxe: TV-MAXE is an application which provides the ability to watch TV stations and listen radio via different streams, such is SopCast. Currently it has a large number of channels, both romanian and international.
SCPlayer: SCPlayer is a simple and lightweight GUI frontend for sopcast supporting only linux GNOME3 platform.
Pysopcast: It is a simple GUI for sopcast made using PyGTK.
totem-sopcast: A totem plugin to let you browse and play sopcast streams.
wxsopcast: A sopcast GUI for linux written in python and wxPython. Note that the channel URL needs to be changed to http://www.sopcast.com/gchlxml at first.
jsopcast: jsopcast is a simple GUI to see P2P TV sopcast made in Java.
If you know of any other GUI frontend for sopcast, please feel free to leave a comment. :)
Read more...
Graphical Frontends To Sopcast Client For Linux
2012-06-11T01:04:00+05:45
Cool Samar
fedora|linux|sopcast|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
fedora,
linux,
sopcast,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday 10 June 2012
Sopcast Player With GUI In Linux
SopCast is a simple, free way to broadcast video and audio or watch the video and listen to radio on the Internet. Adopting P2P(Peer-to-Peer) technology, It is very efficient and easy to use. The GUI for sopcast player for linux works pretty well and this post gives you the step by step process of installation of sopcast player in linux.
Follow the steps as below for easy installation under ubuntu. Instructions should be similar in many variants:

Now everything should work fine. I hope this helps. :)
Read more...
Follow the steps as below for easy installation under ubuntu. Instructions should be similar in many variants:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ su
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/# mkdir sopcast && cd sopcast/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://www.sopcast.com/download/libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# apt-get install gettext python-setuptools libvlc-dev
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd sopcast-player
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make install
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../sp-auth
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/sp-auth# cp sp-sc-auth /usr/bin/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# cp -a libstdc++.so.5* /usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# sopcast-player
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/# mkdir sopcast && cd sopcast/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://www.sopcast.com/download/libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# wget http://sopcast-player.googlecode.com/files/sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sopcast-player-0.8.5.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf sp-auth-3.2.6.tar.gz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# tar -xvf libstdcpp5.tgz
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# apt-get install gettext python-setuptools libvlc-dev
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd sopcast-player
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# make install
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../sp-auth
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/sp-auth# cp sp-sc-auth /usr/bin/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast# cd ../usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# cp -a libstdc++.so.5* /usr/lib/
root@Techgaun:/home/samar/Desktop/sopcast/usr/lib/# sopcast-player

Now everything should work fine. I hope this helps. :)
Read more...
Sopcast Player With GUI In Linux
2012-06-10T23:46:00+05:45
Cool Samar
linux|sopcast|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
linux,
sopcast,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 8 June 2012
Now NTC Hosts Ubuntu Repository For Nepal
As most of the ubuntu users know that the previous nepali repository hosted by Mitra Network Pvt. Ltd. had lots of problem in packages and later went down for a long time. This time, it is NTC who has taken a good initiative and has started providing local ubuntu repository for us.
As seen on foss nepal's mailing list, everybody seems to be happy with the effort of NTC to promote linux and open source software tools in Nepal.
The np.archive.ubuntu.com is now resolving to ubuntu.ntc.net.np now. You can edit your sources.list and choose the nepali repository now. :)
Also, lots of ubuntu distros are available for download. See THIS. Now I can download ubuntu ISO's in around one or two minutes(Thanks NPIX for keeping local traffic local)
In case anyone wants my copy of sources.list file, here it is: sources.list or get it from HERE in case you hate registering on 4shared.
Once you copy the sources.list to /etc/apt/sources.list, make sure to run sudo apt-get update to update the package database.
Read more...
As seen on foss nepal's mailing list, everybody seems to be happy with the effort of NTC to promote linux and open source software tools in Nepal.
The np.archive.ubuntu.com is now resolving to ubuntu.ntc.net.np now. You can edit your sources.list and choose the nepali repository now. :)
Also, lots of ubuntu distros are available for download. See THIS. Now I can download ubuntu ISO's in around one or two minutes(Thanks NPIX for keeping local traffic local)
In case anyone wants my copy of sources.list file, here it is: sources.list or get it from HERE in case you hate registering on 4shared.
Once you copy the sources.list to /etc/apt/sources.list, make sure to run sudo apt-get update to update the package database.
Read more...
Now NTC Hosts Ubuntu Repository For Nepal
2012-06-08T21:49:00+05:45
Cool Samar
news|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
news,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday 27 May 2012
Accelerate Download Speed In Linux Using Axel
Axel is a lightweight command line download accelerator for linux. Axel is a program that downloads a file from a FTP or HTTP server through multiple connection, each connection downloads its own part of the file.
Unlike most other programs, Axel downloads all the data directly to the destination file, using one single thread. It just saves some time at the end because the program doesn't have to concatenate all the downloaded parts.
Axel tries to accelerate downloads by using multiple connections (possibly to multiple servers) for one download. Because of its size, it might be very useful on bootdisks or other small systems as a wget replacement.
One useful implementation of axel is in the apt-fast tool, a fusion of apt-get and axel to accelerate downloads of packages.
Installation under ubuntu and other debian distros: Open the terminal and type:
Similarly, a graphical frontend axel-kapt is also available for download for GUI lovers. Also, flashgot plugin for firefox lets you make use of axel to download files. I should say, axel is a small yet good download accelerator for linux systems.
Read more...
Unlike most other programs, Axel downloads all the data directly to the destination file, using one single thread. It just saves some time at the end because the program doesn't have to concatenate all the downloaded parts.
Axel tries to accelerate downloads by using multiple connections (possibly to multiple servers) for one download. Because of its size, it might be very useful on bootdisks or other small systems as a wget replacement.
One useful implementation of axel is in the apt-fast tool, a fusion of apt-get and axel to accelerate downloads of packages.
Installation under ubuntu and other debian distros: Open the terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install axel
Similarly, a graphical frontend axel-kapt is also available for download for GUI lovers. Also, flashgot plugin for firefox lets you make use of axel to download files. I should say, axel is a small yet good download accelerator for linux systems.
Read more...
Accelerate Download Speed In Linux Using Axel
2012-05-27T21:38:00+05:45
Cool Samar
axel|command line|download|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
axel,
command line,
download,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Monday 2 April 2012
How To Disable Password Prompts For sudo In Ubuntu
If you are one of those linux users who very frequently use the sudo command, you might have been annoyed of entering passwords each time you use this command. However with a very simple tweak, you can change this behaviour and disable the password prompts for the sudo command.
A bit of warning though, do not modify the default behavior of asking for passwords since it would drastically compromise security of your system. Following is the warning given by ubuntu help.
If you disable the sudo password for your account, you will seriously compromise the security of your computer. Anyone sitting at your unattended, logged in account will have complete Root access, and remote exploits become much easier for malicious crackers.
Now you are aware of warning, lets see how this can be done.We need to edit the /etc/sudoers file. Lets first open the file in safe editable mode using the following command:
Using visudo for editing the /etc/sudoers lets us locate the possible errors that may occur while editing the file so always use visudo.
Following is the format of disabling password prompts for specific user.
So if we are to disable password prompts for the user samar, you can make a new line with following entry:
In case you want to let all the users with admin privilege use the sudo command without having to give the password, you can edit the line that says %admin ALL=(ALL) ALL to the following:
Once you add such line for appropriate user, press Ctrl + x and save the changes. You will either have to log out and login back or restart the shell to see the modification in effect.
I hope this is useful. :)
Read more...
A bit of warning though, do not modify the default behavior of asking for passwords since it would drastically compromise security of your system. Following is the warning given by ubuntu help.
If you disable the sudo password for your account, you will seriously compromise the security of your computer. Anyone sitting at your unattended, logged in account will have complete Root access, and remote exploits become much easier for malicious crackers.
Now you are aware of warning, lets see how this can be done.We need to edit the /etc/sudoers file. Lets first open the file in safe editable mode using the following command:
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo visudo
Using visudo for editing the /etc/sudoers lets us locate the possible errors that may occur while editing the file so always use visudo.
Following is the format of disabling password prompts for specific user.
<username> ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL
So if we are to disable password prompts for the user samar, you can make a new line with following entry:
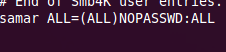
samar ALL=(ALL)NOPASSWD: ALL
In case you want to let all the users with admin privilege use the sudo command without having to give the password, you can edit the line that says %admin ALL=(ALL) ALL to the following:
%admin ALL=(ALL)NOPASSWD: ALL
Once you add such line for appropriate user, press Ctrl + x and save the changes. You will either have to log out and login back or restart the shell to see the modification in effect.
I hope this is useful. :)
Read more...
How To Disable Password Prompts For sudo In Ubuntu
2012-04-02T23:33:00+05:45
Cool Samar
linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Wednesday 28 March 2012
How To Fix NTFS Disk Partition From Linux
If you have problematic NTFS partition in your hard disk, you can fix many of the common NTFS inconsistencies from linux. Linux consists of a set of tools that allow you to manipulate and perform different types of actions on the NTFS partitions. This package is known as ntfsprogs.
If your linux distribution does not consist of the ntfsprogs package, you can install it by using the package manager tool that comes in your distribution or from command line. Debian and ubuntu users can type the following command:
Now to fix the NTFS drive, we must first determine the partition we want to fix. We can use the simplest one, the fdisk utility to determine the partition of hard disk we want to fix. Type the following command to view the list of partitions:
If you have more than one HDDs and want to view partitions of specific HDD, you can always do so by issuing the commands such as sudo fdisk -l /dev/sda or sudo fdisk -l /dev/sdb and so on.
Now lets suppose its /dev/sdb5 we need to fix. We can now use the ntfsfix command that comes in the ntfsprogs package.
Note that it only repairs some fundamental NTFS inconsistencies, resets the NTFS journal file and schedules an NTFS consistency check for the first boot into Windows. You may run ntfsfix on an NTFS volume if you think it was damaged by Windows or some other way and it cannot be mounted.
Read more...
If your linux distribution does not consist of the ntfsprogs package, you can install it by using the package manager tool that comes in your distribution or from command line. Debian and ubuntu users can type the following command:
sudo apt-get install ntfsprogs
Now to fix the NTFS drive, we must first determine the partition we want to fix. We can use the simplest one, the fdisk utility to determine the partition of hard disk we want to fix. Type the following command to view the list of partitions:
sudo fdisk -l
If you have more than one HDDs and want to view partitions of specific HDD, you can always do so by issuing the commands such as sudo fdisk -l /dev/sda or sudo fdisk -l /dev/sdb and so on.
Now lets suppose its /dev/sdb5 we need to fix. We can now use the ntfsfix command that comes in the ntfsprogs package.
sudo ntfsprogs /dev/sdb5
Note that it only repairs some fundamental NTFS inconsistencies, resets the NTFS journal file and schedules an NTFS consistency check for the first boot into Windows. You may run ntfsfix on an NTFS volume if you think it was damaged by Windows or some other way and it cannot be mounted.
Read more...
How To Fix NTFS Disk Partition From Linux
2012-03-28T20:53:00+05:45
Cool Samar
linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|windows|
Comments
Labels:
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10,
windows
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Sunday 11 March 2012
Determine Directory Size From Terminal In Linux [How To]
Sometimes you are working on command line and you want to find the total size of any directory. An instance is while working over SSh. Here is a technique on how you can determine the size of any directory from terminal.
du command lets us estimate the file space usage and can be recursively used for directories as well. This command can also be useful if you want to find the folder sizes of each subdirectories in any specified directory, something that would have been hard to achieve from the GUI.
To find the total size of a directory, use the -sch switch as below:
The screenshot below will help you understand more clearly:
If you would like to see some more details like the size of each subdirectory, use the -hc switch as below:
Check the screenshot below:
The du command provides more advanced stuffs such as exclusions of files and directories and depths for determining size. I hope this helps you. :)
Read more...
du command lets us estimate the file space usage and can be recursively used for directories as well. This command can also be useful if you want to find the folder sizes of each subdirectories in any specified directory, something that would have been hard to achieve from the GUI.
To find the total size of a directory, use the -sch switch as below:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/samar$ du -sch directory_name
The screenshot below will help you understand more clearly:
If you would like to see some more details like the size of each subdirectory, use the -hc switch as below:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/samar$ du -hc directory_name
Check the screenshot below:
The du command provides more advanced stuffs such as exclusions of files and directories and depths for determining size. I hope this helps you. :)
Read more...
Determine Directory Size From Terminal In Linux [How To]
2012-03-11T18:28:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|command prompt|linux|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
command prompt,
linux,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Friday 17 February 2012
5 Cool and Useful Linux Command Line Tricks
Well using linux is fun and working on linux terminal is even more fun. Learning to use linux terminal and commands can prove very useful for personal as well as enterprise purpose. Today I'm going to talk about few cool and crazy linux commands that are less likely to be known by the average computer user.
1) The !$ trick: The !$ is a type of event designator that is present in bash as the feature. I'm not sure if other shells support it but bash does, for sure(I heard event designators are bash-specific). Anyway, !$ saves the last string from the previous command you've entered. The session in bash below shows what it actually does:
So when we give the mkdir test command, the !$ holds the value test So when we do cd !$, !$ is replaced by the string test which is the last string in last entered command.
2) The Don't Save This Command trick: Prepending your command with one or more space(<space>command) will not save the command in the bash history. This trick can be quite useful while doing password related stuffs and while sneaking in your friend's laptop.
3) The Oh! I forgot sudo trick: Well this is one of my favorite tricks and I named it so because I tend to forget to put sudo while running many commands and then I use this trick to prepend sudo at the beginning of the command. Below is the session when I used this trick recently.
As shown above, the !! is just another event designator. The !! actually holds the last used command and this can be alternatively specified as !-1. The !-1 version can be actually generalized to traverse back to history i.e. you can get any command in your history by using !-n convention.
4) The Clean up Terminal trick: Sometimes you open the binary and gibberish data and your terminal looks so ugly and needs some cleanup. In such cases, the command reset can be used which actually does is initialize the terminal.
5) Run previous command by replacing one string with another: Using the syntax ^abc^xyz^, you can run the previous command by replacing the string abc by the string xyz. The example below shows how I used the cat command after using the ls command. Its just an example, you could really make use of this trick for longer commands.
Read more...
1) The !$ trick: The !$ is a type of event designator that is present in bash as the feature. I'm not sure if other shells support it but bash does, for sure(I heard event designators are bash-specific). Anyway, !$ saves the last string from the previous command you've entered. The session in bash below shows what it actually does:
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ mkdir test
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ cd !$
cd test
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ cd !$
cd test
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop/test$
So when we give the mkdir test command, the !$ holds the value test So when we do cd !$, !$ is replaced by the string test which is the last string in last entered command.
2) The Don't Save This Command trick: Prepending your command with one or more space(<space>command) will not save the command in the bash history. This trick can be quite useful while doing password related stuffs and while sneaking in your friend's laptop.
3) The Oh! I forgot sudo trick: Well this is one of my favorite tricks and I named it so because I tend to forget to put sudo while running many commands and then I use this trick to prepend sudo at the beginning of the command. Below is the session when I used this trick recently.
samar@Techgaun:~$ cat /etc/sudoers
cat: /etc/sudoers: Permission denied
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo !!
sudo cat /etc/sudoers
[sudo] password for samar:
*** Content Snipped to preserve length ***
cat: /etc/sudoers: Permission denied
samar@Techgaun:~$ sudo !!
sudo cat /etc/sudoers
[sudo] password for samar:
*** Content Snipped to preserve length ***
As shown above, the !! is just another event designator. The !! actually holds the last used command and this can be alternatively specified as !-1. The !-1 version can be actually generalized to traverse back to history i.e. you can get any command in your history by using !-n convention.
4) The Clean up Terminal trick: Sometimes you open the binary and gibberish data and your terminal looks so ugly and needs some cleanup. In such cases, the command reset can be used which actually does is initialize the terminal.
5) Run previous command by replacing one string with another: Using the syntax ^abc^xyz^, you can run the previous command by replacing the string abc by the string xyz. The example below shows how I used the cat command after using the ls command. Its just an example, you could really make use of this trick for longer commands.
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ ls /etc/hosts
/etc/hosts
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ ^ls^cat^
cat /etc/hosts
/etc/hosts
samar@Techgaun:~/Desktop$ ^ls^cat^
cat /etc/hosts
Read more...
5 Cool and Useful Linux Command Line Tricks
2012-02-17T20:00:00+05:45
Cool Samar
command line|linux|tricks and tips|ubuntu|ubuntu 11.10|
Comments
Labels:
command line,
linux,
tricks and tips,
ubuntu,
ubuntu 11.10
Bookmark this post:blogger tutorials
Social Bookmarking Blogger Widget |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)